Background information: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
| (12 dazwischenliegende Versionen von 2 Benutzern werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
| − | + | {{#set:Has parent page=IMPACT}} | |
| + | ==Objectives== | ||
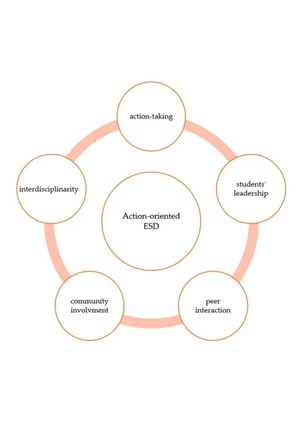
| + | At the core of the IMP>ACT assessment framework are the concepts of action competence (key observable learning outcome of SCCE) and action-orientation (key qualities of teaching, driving learning in SCCE). IMP>ACT will design and validate the framework in a user-centred, iterative approach through small-scale interventions, followed by six large-scale case studies,selected to cover the lifelong learning scope of SCCE. IMP>ACT brings together an interdisciplinary consortium with partners from SCCE research, policy and practice. | ||
| − | + | {{Expander|Deutsch|Im Mittelpunkt des IMP>ACT-Bewertungsrahmens steht die Handlungskompetenz (als wichtigstes Lernergebnis von BNE und Klimabildung) und die Handlungsorientierung (als Schlüsselkompetenz bei Lernenden). IMP>ACT wird den Bewertungsrahmen in einem nutzer:innenzentrierten, iterativen Ansatz durch kleine Interventionen entwickeln und validieren, gefolgt von sechs groß angelegten Fallstudien, die so ausgewählt wurden, dass sie den Bereich des lebenslangen Lernens im Bereich BNE und Klimabildung abdecken. Dabei bringt IMP>ACT ein interdisziplinäres Konsortium bestehend aus Partner:innen aus Forschung, Politik und Praxis zusammen. | |
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Action Competence=== | ||
| − | + | *"Commitment, willingness and ability to take action" | |
| − | " | + | *"All actions are behaviors, but not all behaviors are actions" |
| − | + | [[Datei:Sustainability-11-05994-g003-550.pdf|mini|link=https://wiki.dg-hochn.de/images/7/78/Sustainability-11-05994-g003-550.pdf|alt=(Mogensen & Schnack, 2010, Sass et al., 2020)]] | |
| − | Action: | + | '''Action:''' |
*Decided upon by those who act | *Decided upon by those who act | ||
*Comes from a commitment to/ connection with a controversial issue | *Comes from a commitment to/ connection with a controversial issue | ||
*Deliberated and intended as a contribution to solving that issue | *Deliberated and intended as a contribution to solving that issue | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
(Sinakou et al., 2019, Van Poeck et al., 2023) | (Sinakou et al., 2019, Van Poeck et al., 2023) | ||
| − | More readings on action competence | + | ===More readings on action competence=== |
*Sinakou, Donche, Boeve-de Pauw, & Van Petegem. (2019). Designing Powerful Learning Environments in Education for Sustainable Development: A Conceptual Framework. Sustainability, 11(21), 5994. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11215994 | *Sinakou, Donche, Boeve-de Pauw, & Van Petegem. (2019). Designing Powerful Learning Environments in Education for Sustainable Development: A Conceptual Framework. Sustainability, 11(21), 5994. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11215994 | ||
*Sass, W., De Maeyer, S., Boeve-de Pauw, J., & Van Petegem, P. (2024). Effectiveness of education for sustainability: The importance of an action-oriented approach. Environmental Education Research, 30(4), 479–498. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504622.2023.2229543 | *Sass, W., De Maeyer, S., Boeve-de Pauw, J., & Van Petegem, P. (2024). Effectiveness of education for sustainability: The importance of an action-oriented approach. Environmental Education Research, 30(4), 479–498. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504622.2023.2229543 | ||
| Zeile 27: | Zeile 28: | ||
*European Commission. Joint Research Centre. (2020). Sustainability competences: A systematic literature review. Publications Office. https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2760/200956 | *European Commission. Joint Research Centre. (2020). Sustainability competences: A systematic literature review. Publications Office. https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2760/200956 | ||
| − | + | ==Methodology== | |
IMP>ACT applies a participatory design approach to its research and development activities, including relevant knowledge actors and users by means of co-design, co-creation and co-assessment. Through participatory design research, we aim to engage these stakeholders in the design process of the IMP>ACT assessment framework, to ensure that the framework is effective, relevant, and inclusive of their contexts and needs. Our approach to participatory design research involves identifying and recruiting stakeholders, co-designing research questions, collecting, analysing, and interpreting data, knowledge dissemination, and enacting change. | IMP>ACT applies a participatory design approach to its research and development activities, including relevant knowledge actors and users by means of co-design, co-creation and co-assessment. Through participatory design research, we aim to engage these stakeholders in the design process of the IMP>ACT assessment framework, to ensure that the framework is effective, relevant, and inclusive of their contexts and needs. Our approach to participatory design research involves identifying and recruiting stakeholders, co-designing research questions, collecting, analysing, and interpreting data, knowledge dissemination, and enacting change. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Expander|Deutsch|IMP>ACT wendet bei seinen Forschungs- und Entwicklungsaktivitäten einen partizipativen Designansatz an, der relevante Wissensakteur:innen und Nutzer:innen durch Co-Design, Co-Kreation und Co-Assessment einbezieht. Durch partizipative Designforschung wollen wir diese Interessengruppen in den Designprozess des IMP>ACT-Bewertungsrahmens integrieren, um sicherzustellen, dass der Rahmen effektiv ist und die Kontexte sowie Bedürfnisse der Interessengruppen berücksichtigt werden. Unser Ansatz der partizipativen Designforschung umfasst die Identifizierung und Rekrutierung von relevanten Stakeholdern, die Mitgestaltung von Forschungsfragen, das Sammeln, Analysieren und Interpretieren von Daten, die Wissensverbreitung und das Vorantreiben eines Wandels. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | [[Kategorie:Projekt]][[Kategorie:IMPACT]] | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 23. Mai 2024, 11:49 Uhr
Objectives
At the core of the IMP>ACT assessment framework are the concepts of action competence (key observable learning outcome of SCCE) and action-orientation (key qualities of teaching, driving learning in SCCE). IMP>ACT will design and validate the framework in a user-centred, iterative approach through small-scale interventions, followed by six large-scale case studies,selected to cover the lifelong learning scope of SCCE. IMP>ACT brings together an interdisciplinary consortium with partners from SCCE research, policy and practice.
Im Mittelpunkt des IMP>ACT-Bewertungsrahmens steht die Handlungskompetenz (als wichtigstes Lernergebnis von BNE und Klimabildung) und die Handlungsorientierung (als Schlüsselkompetenz bei Lernenden). IMP>ACT wird den Bewertungsrahmen in einem nutzer:innenzentrierten, iterativen Ansatz durch kleine Interventionen entwickeln und validieren, gefolgt von sechs groß angelegten Fallstudien, die so ausgewählt wurden, dass sie den Bereich des lebenslangen Lernens im Bereich BNE und Klimabildung abdecken. Dabei bringt IMP>ACT ein interdisziplinäres Konsortium bestehend aus Partner:innen aus Forschung, Politik und Praxis zusammen.
Action Competence
- "Commitment, willingness and ability to take action"
- "All actions are behaviors, but not all behaviors are actions"
Action:
- Decided upon by those who act
- Comes from a commitment to/ connection with a controversial issue
- Deliberated and intended as a contribution to solving that issue
(Sinakou et al., 2019, Van Poeck et al., 2023)
More readings on action competence
- Sinakou, Donche, Boeve-de Pauw, & Van Petegem. (2019). Designing Powerful Learning Environments in Education for Sustainable Development: A Conceptual Framework. Sustainability, 11(21), 5994. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11215994
- Sass, W., De Maeyer, S., Boeve-de Pauw, J., & Van Petegem, P. (2024). Effectiveness of education for sustainability: The importance of an action-oriented approach. Environmental Education Research, 30(4), 479–498. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504622.2023.2229543
- Sass, W., Boeve-de Pauw, J., Olsson, D., Gericke, N., De Maeyer, S., & Van Petegem, P. (2020). Redefining action competence: The case of sustainable development. The Journal of Environmental Education, 51(4), 292–305. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958964.2020.1765132
- Schönstein, R. F., & Budke, A. (2024). Teaching action competence in education for sustainable development – a qualitative study on teachers’ ideas, opinions, attitudes and self-conceptions. Frontiers in Education, 8, 1256849. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2023.1256849
- European Commission. Joint Research Centre. (2020). Sustainability competences: A systematic literature review. Publications Office. https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2760/200956
Methodology
IMP>ACT applies a participatory design approach to its research and development activities, including relevant knowledge actors and users by means of co-design, co-creation and co-assessment. Through participatory design research, we aim to engage these stakeholders in the design process of the IMP>ACT assessment framework, to ensure that the framework is effective, relevant, and inclusive of their contexts and needs. Our approach to participatory design research involves identifying and recruiting stakeholders, co-designing research questions, collecting, analysing, and interpreting data, knowledge dissemination, and enacting change.
IMP>ACT wendet bei seinen Forschungs- und Entwicklungsaktivitäten einen partizipativen Designansatz an, der relevante Wissensakteur:innen und Nutzer:innen durch Co-Design, Co-Kreation und Co-Assessment einbezieht. Durch partizipative Designforschung wollen wir diese Interessengruppen in den Designprozess des IMP>ACT-Bewertungsrahmens integrieren, um sicherzustellen, dass der Rahmen effektiv ist und die Kontexte sowie Bedürfnisse der Interessengruppen berücksichtigt werden. Unser Ansatz der partizipativen Designforschung umfasst die Identifizierung und Rekrutierung von relevanten Stakeholdern, die Mitgestaltung von Forschungsfragen, das Sammeln, Analysieren und Interpretieren von Daten, die Wissensverbreitung und das Vorantreiben eines Wandels.